Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
A Comprehensive Study Assessing the Transformative Role of Artificial Intelligence in India\'s Governance Policy Framework
Authors: Saurabh Bansal, Dr. Neelesh Jain
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.54973
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has gained significant prominence worldwide, and India is actively embracing its potential for transforming various sectors. This paper comprehensively studies the intersection between artificial intelligence and Indian government policies. It explores the opportunities, challenges, and implications of AI implementation in the Indian context, and discusses the evolving role of the Indian government in harnessing AI technologies. The paper addresses the challenges and risks associated with AI implementation in India, including ethical considerations, socioeconomic implications, privacy concerns, workforce capacity building, and infrastructure requirements. This section underscores the need for appropriate policies and regulatory frameworks to address these challenges effectively. The paper further examines the Indian government\'s policies and initiatives on AI, including the national AI strategy, policy frameworks, AI centres of excellence, startup ecosystem, and international collaboration efforts. It delves into key policy considerations such as data governance, ethical and responsible AI, regulation and standards, skills development, and inclusivity.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
A. Background
The term ‘Artificial Intelligence’ means a machine-based system that can, for a given set of human-defined objectives, make predictions, recommendations or decisions influencing real or virtual environments. The government focuses on AI because it is at the centre of the global technological revolution; advances in AI technology present both great opportunities and challenges. Artificial intelligence, the development of computer systems to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as learning and decision-making, has the potential to transform and spur innovation across industry and government. Although the government is confident that AI can improve citizens’ lives, it still struggles with scaling AI for large-scale deployment. Increasing the government’s AI maturity requires pairing human and technical capabilities with strategy and governance.
There is a “National Strategy on AI” which has been announced by the NITI Aayog (an apex think-tank of the Indian government) in 2018. Before this Strategy, there has been a report submitted by the AI Task Force constituted by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry in January 2018 The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) also constituted four expert committees in February 2018 to suggest ways to promote AI and to develop a policy framework for India. These committees dealt with the following four areas: Platforms and data for AI; leveraging AI for identifying National Missions in key sectors; mapping technological capabilities, and key policy enablers required across sectors; skilling and re-skilling, R&D; and cyber security, safety, legal and ethical issues.
B. Artificial Intelligence as an Emerging Priority Area
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative technology with significant implications for various sectors, including governance and public administration. In India, the government recognizes the potential of AI to drive economic growth, improve service delivery, and enhance governance efficiency. As a result, understanding the intersection between AI and Indian government policies is of utmost importance. The study of AI and Indian government policies is significant for several reasons:
- Harnessing AI for Economic Growth: AI has the potential to significantly contribute to India's economic growth by fostering innovation, improving productivity, and creating new job opportunities. Analyzing government policies related to AI helps identify strategies and initiatives aimed at maximizing the economic benefits of AI adoption.
- Strengthening Governance and Service Delivery: AI can enhance the efficiency, transparency, and effectiveness of government operations, leading to improved governance and service delivery. A comprehensive study of government policies allows for the identification of initiatives targeting AI implementation in areas such as healthcare, agriculture, education, and public service delivery.
- Addressing Ethical and Societal Implications: As AI technologies advance, ethical considerations, privacy concerns, and societal implications become critical issues. Analyzing government policies provides insights into the steps taken to address these concerns, promote responsible AI practices, and ensure that AI deployment aligns with societal values and interests.
- Collaboration and International Cooperation: AI is a global phenomenon, and collaboration and cooperation between countries are vital for sharing knowledge, best practices, and regulatory frameworks. Analyzing Indian government policies related to international collaboration provides an understanding of the efforts made to foster global partnerships, participate in international AI initiatives, and contribute to the development of international standards.
C. Benefits of AI in Governance
Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers numerous benefits for Indian government operations, transforming the way public services are delivered, enhancing efficiency, and improving decision-making processes. The following are key benefits of AI in Indian government operations:
- Enhanced Efficiency: AI technologies can automate routine and repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources to focus on more complex and value-added activities. By automating processes such as data entry, document processing, and administrative tasks, AI improves operational efficiency and reduces the burden of manual work.
- Improved Service Delivery: AI enables governments to deliver services more effectively and efficiently. Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI can handle citizen queries, provide personalized assistance, and streamline the delivery of information and services. This improves access to government services, reduces response times, and enhances the overall citizen experience.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Government agencies generate vast amounts of data. AI analytics tools can process and analyze this data to derive valuable insights, enabling data-driven decision-making. By leveraging AI algorithms and machine learning techniques, governments can gain actionable intelligence, identify patterns, and make informed policy decisions based on evidence.
- Public Safety and Security: AI has the potential to enhance public safety and security in various ways. AI-powered surveillance systems can detect and identify potential threats, monitor public spaces, and improve law enforcement efforts. Predictive analytics models can also help in identifying patterns and trends related to criminal activities, enabling proactive measures to ensure public safety.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: AI algorithms can optimize government operations' resource allocation and planning processes. For instance, AI can assist in demand forecasting for public services, resource allocation for infrastructure development, and route optimization for transportation systems. This ensures that resources are utilized efficiently and effectively, leading to cost savings and improved service delivery.
- Fraud Detection and Prevention: AI techniques, such as anomaly detection and pattern recognition, can be employed to identify and prevent fraudulent activities within government systems. By analyzing large volumes of data and detecting irregularities, AI-powered systems can help in preventing financial fraud, tax evasion, and other forms of corruption.
- Decision Support Systems: AI can support government officials in making informed decisions by providing them with real-time insights and analysis. AI-powered decision support systems can consider various factors, scenarios, and data sources to recommend optimal solutions, policy options, or courses of action. This assists policymakers and administrators in formulating evidence-based decisions.
By leveraging AI technologies, Indian government operations can achieve greater efficiency, improved service delivery, and evidence-based decision-making. These benefits ultimately contribute to more effective governance, better utilization of resources, and enhanced public trust in government services.
II. POLICY FRAMEWORKS AND GUIDELINES
To ensure responsible and effective implementation of AI in Indian government operations, the development and implementation of policy frameworks and guidelines are crucial. These frameworks provide a roadmap for AI adoption, address ethical considerations, promote transparency, and ensure accountability. Some key policy frameworks and guidelines for AI in the Indian government include:
- National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence: The Indian government has formulated a national strategy for AI that outlines the vision, objectives, and key focus areas for AI adoption. The strategy provides a comprehensive framework for AI implementation across sectors, emphasizing research and development, capacity building, ethical considerations, and collaboration with industry and academia.
- Ethical Guidelines for AI: The government has emphasized the need for ethical guidelines to guide AI deployment. These guidelines promote fairness, transparency, accountability, and privacy in AI systems. They address concerns related to bias, discrimination, and the responsible use of AI technologies. Ethical guidelines ensure that AI systems align with societal values and are deployed in a manner that benefits all citizens.
- Data Governance and Privacy: Policies and guidelines related to data governance and privacy are essential for AI implementation. These frameworks address issues such as data collection, storage, sharing, and anonymization. They ensure that citizen data is protected, privacy is respected, and data usage is in compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
- Regulatory Framework for AI: The government is working on developing a regulatory framework to govern AI adoption. This framework aims to address risks, set standards, and ensure the responsible use of AI technologies. It may include regulations on data usage, algorithmic transparency, cyber security, accountability, and liability. The regulatory framework provides a legal basis for AI implementation and promotes trust in AI systems.
- Interdisciplinary Research and Collaboration: The government encourages interdisciplinary research and collaboration between various stakeholders, including government agencies, research institutions, industry, and civil society organizations. These collaborations help in developing AI policies, identifying best practices, and fostering innovation in AI technologies and applications.
- International Collaboration: Policies are being developed to foster international collaboration in AI. The government seeks to collaborate with international organizations, governments, and industry partners to share knowledge, best practices, and regulatory approaches. These collaborations help in aligning AI policies with global standards and facilitate technology transfer.
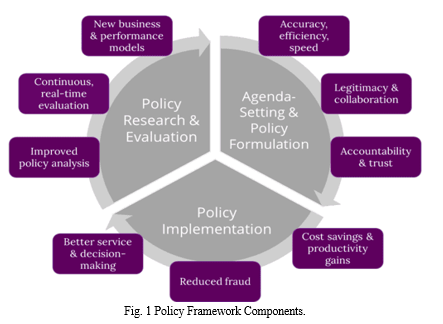
These policy frameworks and guidelines provide a foundation for the responsible and effective adoption of AI in Indian government operations. They ensure that AI technologies are deployed ethically, transparently, and with consideration for privacy and societal impact. Continual assessment and evolution of these policies are crucial to address emerging challenges and opportunities in the AI landscape.
III. INDIAN GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES ON ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
A. National AI Strategy
The India National AI Strategy is a comprehensive framework developed by the Indian government to leverage the potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for economic growth, social welfare, and governance efficiency. The strategy aims to position India as a global leader in AI by fostering innovation, building a skilled workforce, and creating an enabling environment for AI adoption across sectors. The key objectives of the National AI Strategy include:
- Enhancing Economic Growth: The strategy seeks to drive economic growth by promoting AI-driven innovation, fostering entrepreneurship, and supporting the growth of AI startups and enterprises. It aims to attract investments in AI research, development, and deployment to boost the Indian economy.
- Improving Social Welfare: The strategy focuses on leveraging AI to address social challenges and improve the quality of life for citizens. It aims to deploy AI technologies in areas such as healthcare, agriculture, education, and public service delivery to enhance the accessibility, affordability, and efficiency of services.
- Building a Skilled Workforce: Recognizing the importance of human capital in AI, the strategy emphasizes skilling and capacity-building initiatives. It aims to develop a robust talent pool of AI professionals through training programs, academic collaborations, and industry partnerships to meet the growing demand for AI expertise.
- Promoting Research and Innovation: The strategy emphasizes the importance of research and development in AI. It aims to establish AI research institutes, centres of excellence, and innovation hubs to facilitate cutting-edge research, foster collaboration between academia and industry, and drive technological advancements in AI.
- Ensuring responsible AI adoption: The strategy acknowledges the ethical considerations associated with AI and emphasizes the need for responsible AI practices. It aims to establish regulatory frameworks and guidelines to address concerns related to privacy, security, fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI systems.
To implement the National AI Strategy, (Niti Aayog’s National Strategy For AI: #AIFORALL) the Indian government has set up various mechanisms such as the National AI Mission, AI research institutes, and centres. It also focuses on public-private partnerships, collaboration with international organizations, and fostering an innovation-friendly ecosystem to support AI initiatives. The National AI Strategy presents significant opportunities for India in terms of economic development, societal benefits, and governance efficiency. However, it also poses challenges, including ethical considerations, data privacy, skill gaps, inclusivity, and infrastructure requirements. Addressing these challenges and effectively implementing the strategy will be crucial for India's success in harnessing the potential of AI to drive sustainable development and meet the needs of its citizens.
B. AI Centers of Excellence
AI Centers of Excellence (CoEs) are specialized institutions or programs that aim to advance research, development, and application of AI in specific domains or sectors. These centres serve as hubs of expertise, collaboration, and innovation, bringing together academia, industry, and government stakeholders to drive AI-related initiatives. The primary objectives of AI Centers of Excellence include:
- Research and Development: AI CoEs focus on conducting cutting-edge research to advance the understanding and capabilities of AI technologies. They facilitate collaborations between researchers, scientists, and experts to explore new AI algorithms, methodologies, and applications. This research contributes to the development of AI models, frameworks, and solutions that can address real-world challenges.
- Innovation and Technology Transfer: AI CoEs foster an environment of innovation and entrepreneurship. They support startups, enterprises, and industry partners in developing and commercializing AI-driven products, services, and solutions. These centres often provide resources, mentorship, and incubation facilities to promote the growth of AI-based ventures.
- Skills Development and Education: AI CoEs play a crucial role in building a skilled AI workforce. They offer training programs, workshops, and courses to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to work with AI technologies. By providing educational resources and promoting collaboration between academia and industry, AI CoEs help bridge the skills gap in AI-related disciplines.
- Policy Development and Regulation: AI CoEs contribute to the development of policies and regulations related to AI. They engage with policymakers, legal experts, and industry leaders to shape guidelines and ethical frameworks for responsible AI adoption. These centres facilitate discussions on privacy, security, fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI systems, ensuring that the technology is implemented in a manner that aligns with societal values and interests.
- Collaboration and Networking: AI CoEs serve as platforms for collaboration and networking within the AI community. They encourage interdisciplinary cooperation and knowledge sharing among researchers, industry professionals, and government officials. By facilitating partnerships and collaborations, these centres enable the exchange of ideas, expertise, and resources, fostering a vibrant AI ecosystem.
AI Centers of Excellence can be established at national, regional, or sector-specific levels, depending on the focus area and goals. They act as catalysts for AI-driven innovation, fostering the adoption of AI technologies in various sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, finance, transportation, and public administration. Through their activities, AI CoEs contribute to economic growth, societal well-being, and the development of responsible and ethical AI practices.
C. Startup Ecosystem and Innovation: Way to Technology-Enabled Economy
The startup ecosystem and innovation play a crucial role in driving economic growth, fostering technological advancements, and promoting entrepreneurship. This dynamic environment provides a platform for startups, entrepreneurs, and innovators to transform ideas into viable businesses and disruptive solutions. Key aspects of the startup ecosystem and innovation include:
- Entrepreneurial Culture: The startup ecosystem cultivates an entrepreneurial culture that encourages risk-taking, creativity, and innovation. It promotes an environment where individuals are inspired to identify and address market gaps, develop new technologies, and disrupt traditional industries.
- Incubators and Accelerators: Incubators and accelerators provide critical support and resources to startups. They offer mentoring, networking opportunities, office spaces, access to experts, and guidance on business development, marketing, and strategy. These programs help startups refine their ideas, build viable business models, and accelerate their growth trajectory.
- Collaboration and Networking: The startup ecosystem promotes collaboration and networking among entrepreneurs, investors, industry experts, and academia. Startup events, conferences, and meet-ups facilitate knowledge sharing, idea exchange, and partnerships. This collaboration fosters innovation, enables access to expertise, and creates opportunities for business collaborations and market expansion.
- Regulatory Support: Governments play a significant role in nurturing the startup ecosystem by implementing policies and regulations that support entrepreneurship and innovation. These policies may include tax incentives, streamlined business registration processes, intellectual property protection, and supportive regulatory frameworks. Such support enables startups to navigate legal complexities and focus on their core business activities.
- Knowledge Transfer and Research: Collaboration between startups and research institutions promotes knowledge transfer and technology commercialization. Startups often leverage research findings, patents, and expertise from academic institutions to develop innovative solutions. Conversely, research institutions benefit from startups' agility and market-oriented approach, driving the practical application of their research.
The startup ecosystem and innovation are vital components of economic development and job creation. They contribute to technological advancements, promote entrepreneurship, and foster a culture of innovation. By supporting startups, fostering collaboration, and creating a conducive environment, the ecosystem drives economic growth, attracts talent, and positions a country or region as a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship
D. International Collaboration
International collaboration plays a crucial role in driving advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) in India. It enables knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and the establishment of global partnerships to foster AI innovation and development. International collaboration in AI in India encompasses various aspects, including research collaboration, policy cooperation, talent exchange, and joint projects. Key aspects of international collaboration for AI in India include:
- Research Collaboration: Collaborations between Indian research institutions and international counterparts facilitate the exchange of knowledge, expertise, and research findings in AI. These collaborations enable researchers to work together on cutting-edge AI projects, share resources, and leverage diverse perspectives to address complex challenges. Research collaboration enhances the depth and breadth of AI research in India and promotes scientific advancements.
- Talent Exchange and Mobility: International collaboration enables the exchange of talent between India and other countries. It facilitates the movement of researchers, AI professionals, and students, fostering a global learning environment. This exchange of talent promotes the sharing of best practices, cross-cultural understanding, and the development of a diverse AI workforce with a global perspective.
- Policy Cooperation: Collaborating with international organizations, governments, and industry leaders allows India to align its AI policies and strategies with global trends and best practices. International cooperation in policy development and regulation assists in addressing common challenges such as privacy, security, ethical considerations, and AI governance. It also helps India leverage international frameworks and standards in shaping its own AI policies.
- Funding and Investment: International collaboration opens doors for access to global funding and investment opportunities in AI for Indian startups, researchers, and enterprises. Partnerships with international investors, venture capital firms, and innovation ecosystems provide financial support and resources to fuel the growth of AI initiatives in India. This collaboration stimulates entrepreneurship, innovation, and economic development.
- Joint Projects and Initiatives: International collaboration often involves joint projects and initiatives focused on specific AI applications or domains. These projects bring together expertise, resources, and diverse perspectives to tackle complex problems, drive innovation, and accelerate AI deployment. Joint projects may include AI-driven solutions for healthcare, agriculture, smart cities, climate change, and social welfare.
- Standardization and Ethical Frameworks: Collaborating with international bodies and organizations helps India align its AI practices with global standards and ethical frameworks. International collaboration facilitates the exchange of knowledge on AI ethics, responsible AI deployment, and the mitigation of biases and risks. This cooperation ensures that India's AI initiatives adhere to globally accepted principles and guidelines.
International collaboration for AI in India is instrumental in fostering innovation, driving research and development, and positioning India as a global AI hub. It promotes cross-border knowledge exchange, technology transfer, and the creation of global networks. By leveraging international collaborations, India can accelerate AI advancements, address societal challenges, and achieve sustainable development goals.
|
S. No. |
Sector |
Expected outcome |
|
1 |
Health care |
Increase in affordability and access to quality healthcare |
|
2 |
Agriculture |
Increase in agricultural produce and framers’ earnings, along with the reduction in wastage of resources |
|
3 |
Education |
Increase in access and improvement in the quality of education |
|
4 |
Smart cities and infrastructure |
Efficient and connectivity for the growing urban population |
|
5 |
Smart mobility and transformation |
Improvement in prevailing traffic and congestion conditions and implementation of smarter and safer transportation modes |
Fig. 2 Five sectors focused on, in the 2018 Indian strategy for AI (NITI Aayog, 2018)
E . National AI Mission
The National AI Mission in India is a prominent initiative aimed at driving AI research, innovation, and application across various sectors. It serves as a key pillar of India's AI strategy, focusing on advancing AI technologies, building AI capabilities, and fostering a robust AI ecosystem. The National AI Mission comprises several components and initiatives to accelerate AI adoption and development. The objectives of the mission are:
- Promote AI research and development.
- Catalyze AI-led innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Create a skilled workforce in AI technologies.
- Develop AI applications for societal impact.
a. AI Research Institutes and Centers: The National AI Mission focuses on establishing AI research institutes and centres of excellence. These institutes aim to nurture cutting-edge research, develop AI models and algorithms, and drive innovation in AI technology. The institutes facilitate collaborations between academia, industry, and government to advance AI research and translate it into practical applications.
b. AI Innovation Hubs and Startups: The National AI Mission promotes the creation of AI innovation hubs and supports AI-driven startups. These hubs provide a nurturing environment for AI startups, offering mentorship, resources, and infrastructure to foster innovation. They facilitate the development and commercialization of AI-based products and solutions, driving entrepreneurship and economic growth.
c. AI Skilling and Capacity Building: The National AI Mission emphasizes the development of a skilled workforce in AI technologies. It focuses on capacity-building initiatives, such as training programs, certifications, and AI-specific courses. These efforts aim to equip individuals with the necessary skills to work with AI technologies and drive AI adoption in various sectors.
d. Collaboration and Partnerships: The National AI Mission promotes collaboration between government, industry, academia, and international organizations. It seeks to create a vibrant AI ecosystem by fostering partnerships, encouraging knowledge exchange, and leveraging international expertise. Collaboration with industry players facilitates technology transfer, commercialization, and the implementation of AI solutions at scale.
The National AI Mission plays a pivotal role in accelerating AI development and adoption in India. It focuses on research, innovation, skilling, and societal impact, with an emphasis on collaboration and partnerships. Through the National AI Mission, India aims to position itself as a global leader in AI, fostering economic growth, technological advancement, and improved public services.
IV. CHALLENGES AND RISKS: AREAS OF CONCERN
Implementing AI in government operations also presents various challenges and risks that need to be addressed for successful adoption and responsible use. Some of the key challenges and risks include:
- Ethical Considerations: AI systems must adhere to ethical principles, ensuring fairness, transparency, accountability, and respect for privacy. The use of AI in decision-making processes must be unbiased and avoid discrimination or undue bias towards certain groups or individuals. Establishing ethical guidelines and frameworks becomes crucial to mitigate these risks.
- Skilled Workforce and Capacity Building: The successful implementation of AI in government requires a skilled workforce with expertise in AI technologies and data analytics. There is a need to bridge the skill gap by investing in training programs, reskilling initiatives, and educational reforms to ensure that government personnel have the necessary knowledge to work with AI systems effectively.

3. Data Quality and Availability: AI systems rely heavily on high-quality, diverse data for accurate analysis and decision-making. However, there can be challenges in terms of quality, consistency and accessibility when it comes to Indian government data. Ensuring reliable data availability and eliminating data biases and gaps is critical to the adoption of AI in government operations.
4. Privacy and Data Protection: The use of AI technologies involves the processing and analysis of large volumes of personal and sensitive data. Protecting citizen privacy and ensuring data security are critical concerns. Developing robust data protection frameworks, implementing privacy-enhancing technologies, and establishing mechanisms for informed consent and data governance are necessary to mitigate privacy risks.
5. Transparency and Explainability: AI algorithms often operate as black boxes, making it challenging to understand how decisions are made. In government operations, transparency and explainability are crucial to maintaining public trust. Efforts should be made to develop AI systems that are transparent, and accountable, and provide explanations for the decisions and recommendations they produce.
6. Infrastructure and Connectivity: The successful implementation of AI relies on robust infrastructure, including high-speed internet connectivity, data storage capabilities, and computational power. Ensuring that adequate infrastructure is available across regions, including rural areas, is essential to enable seamless AI implementation in government operations.
Addressing these challenges and risks requires a comprehensive approach involving policy frameworks, capacity building, stakeholder engagement, and collaboration between government, industry, academia, and civil society. By proactively addressing these challenges, the Indian government can harness the transformative potential of AI while ensuring responsible and inclusive AI deployment.
V. FUTURE DIRECTIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
A. Strengthening AI Infrastructure
- Invest in robust and scalable AI infrastructure, including high-performance computing resources and cloud platforms.
- Improve connectivity and network infrastructure to ensure seamless AI implementation, especially in rural areas.
- Foster public-private partnerships to leverage private sector expertise and resources for infrastructure development.
B. Promoting Research and Innovation
- Increase funding for AI research and development, with a focus on interdisciplinary collaborations and emerging AI technologies.
- Establish research grants, fellowships, and scholarships to attract and retain top AI talent.
- Encourage industry-academia collaborations to bridge the gap between research and practical implementation.
C. Policy Coherence and Implementation
- Ensure coherence and consistency in AI-related policies across government departments and agencies.
- Establish mechanisms for regular evaluation, monitoring, and review of AI policies to assess their effectiveness and address emerging challenges.
- Foster coordination and collaboration between different government bodies involved in AI governance and implementation.
D. Public-Private Partnerships
- Encourage partnerships between the government and private sector entities to drive AI innovation, research, and deployment.
- Facilitate technology transfer and knowledge sharing between industry and government for effective AI implementation.
- Develop mechanisms for joint projects, funding collaborations, and sharing of resources and expertise.
E. Ethical and Inclusive AI
- Strengthen ethical guidelines and frameworks for AI development and deployment, ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability.
- Promote the development of AI systems that are unbiased, free from discrimination, and address societal challenges.
- Ensure inclusivity by considering diverse perspectives and addressing potential biases in AI algorithms and datasets.
F. Skilling and Education
- Expand AI-focused skilling programs to build a larger pool of AI professionals and equip the existing workforce with AI competencies.
- Foster collaborations between educational institutions, industry, and government to develop AI-specific curricula and training programs.
- Encourage lifelong learning and continuous up-skilling to keep pace with the evolving AI landscape.
G. International Collaboration
- Strengthen collaboration with international organizations, governments, and research institutions for knowledge sharing and harmonization of AI policies.
- Participate in global AI initiatives and standardization efforts to align with international best practices.
- Foster international research collaborations and technology exchanges to leverage global expertise and advancements in AI.
By focusing on these future directions and recommendations, the government can foster a conducive environment for AI innovation, responsible implementation, and societal impact. This will enable us to fully harness the potential of AI, drive economic growth, and improve public services while ensuring ethical, inclusive, and sustainable AI adoption.
Conclusion
The paper aims to provide a comprehensive study of the impact of artificial intelligence on Indian government policies. The paper explores the concepts of AI and its applications in India, emphasizing its potential benefits in government operations such as enhanced efficiency, automation, data-driven decision-making, and public service innovation. The paper concludes with future directions and recommendations for the development of AI governance frameworks in India. It emphasizes the need to strengthen AI infrastructure, promote research and innovation, ensure policy coherence and implementation, foster public-private partnerships, and prioritize ethical and inclusive AI practices. In conclusion, this study paper provides valuable insights into the intersection of artificial intelligence and Indian government policies. Ultimately, the paper aims to contribute to the development of effective and responsible AI governance frameworks in India.
References
[1] Pencheva, I., Esteve, M., & Jankin, S. M. (2018, June 12). Big Data and AI – A transformational shift for government: So, what next for research? Political Science Public Policy and Administration. [2] Sharma, G. D., Yadav, A., & Chopra, R. (2019). Artificial intelligence and effective governance: A review, critique, and research agenda. University School of Management Studies, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, Dwarka Sector 16-C, New Delhi, India. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sftr.2019.100004 [3] Marda, V. (2018, October 15). Artificial intelligence policy in India: a framework for engaging the limits of data-driven decision-making. Royal Society. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2018.0087 [4] Sharma, G. D., Yadav, A., & Chopra, R. (2019). Artificial intelligence and effective governance: A review, critique, and research agenda. University School of Management Studies, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, New Delhi. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sftr.2019.100004 [5] Chatterjee, S. (2020). AI strategy of India: policy framework, adoption challenges, and actions for government. Transforming Government: People, Process, and Policy, 14(5). [6] Elias, J. (2020). India’s AI journey: the story so far. Retrieved from https://indiaai.gov.in/article/india-s-ai-journey-the-story-so-far [7] Feijoo, C., Kwon, Y., Bauer, J. M., Bohlin, E., Howell, B., Jain, R., Potgieter, P., et al. (2020). Harnessing artificial intelligence (AI) to increase wellbeing for all: the case for new technology diplomacy. Telecommunications Policy, 44(6), 101988. [8] Kalyanakrishnan, S., Panicker, R. A., Natarajan, S., & Rao, S. (2018). Opportunities and challenges for artificial intelligence in India. In Proceedings of the 2018 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society (pp. 164-170). [9] NASSCOM. (2021). AI game changers: accelerating India with innovation. Retrieved from https://digitalindia.gov.in [10] NITI Aayog. (2018). Discussion paper: a national strategy for Artificial Intelligence. Retrieved from https://niti.gov.in/writereaddata/files/document_publication/NationalStrategy-for-AI-Discussion-Paper.pdf [11] NITI Aayog. (2021). Responsible AI #AIForAll – Approach document for India: part 2 – Operationalizing principles for responsible AI, August 2021. Retrieved from www.niti.gov.in [12] Jain, N., Agnihotri, B. P., & Verma, A. (2013). Impact Assessment of E-Governance in India. International Journal of Engineering and Management Research, 3(6), 128-131.
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Saurabh Bansal, Dr. Neelesh Jain. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET54973
Publish Date : 2023-07-24
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

